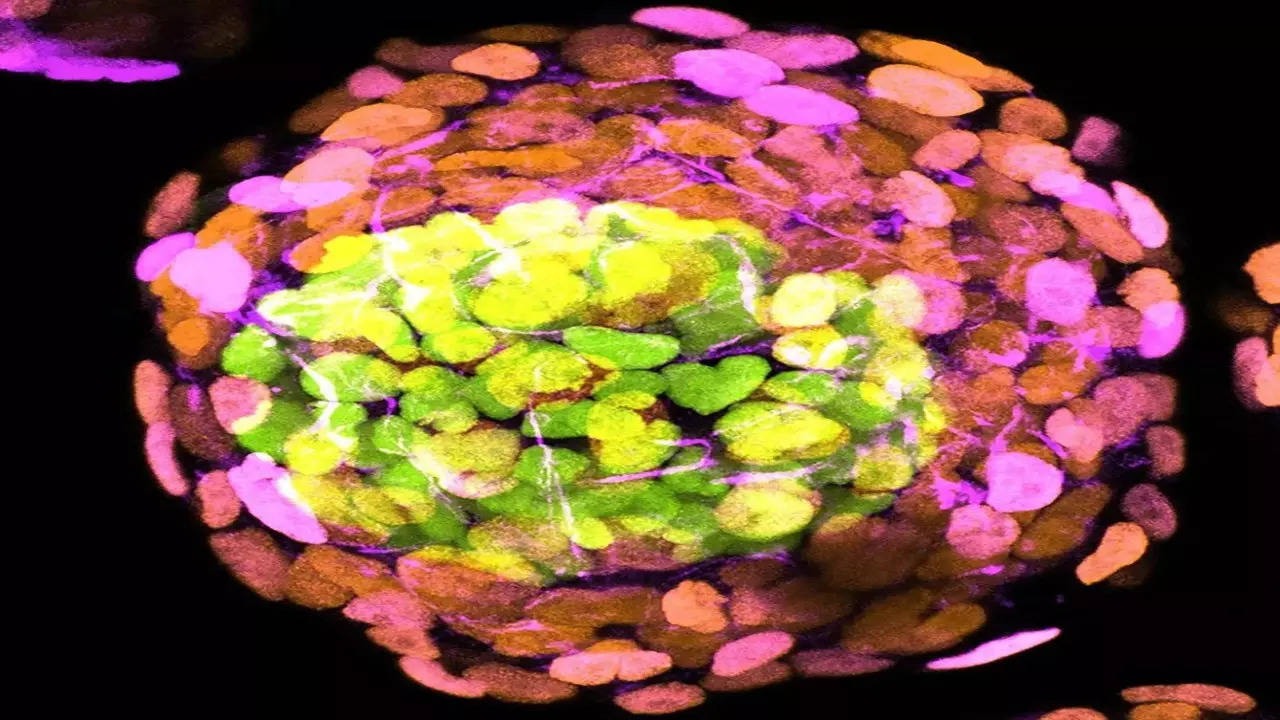
Offering hope for research on miscarriage and birth defects, scientists have grown human embryo-like structures without using sperm, eggs or a womb. A research team, headed by Prof Jacob Hanna at the Weizmann Institute of Science, claims to have “created complete models of human embryos from stem cells cultured in the lab – and managed to grow them outside the womb up to day 14”.
What sets this research apart from others is its utilization of chemically modified rather than genetically modified embryonic stem cells, resulting in models that more closely resemble genuine human embryos, complete with a yolk sac and amniotic cavity.
These resemblances could make these models particularly valuable for studying conditions such as miscarriage, birth defects, and infertility, according to James Briscoe from Britain’s Francis Crick Institute. Briscoe, a principal group leader and associate research director at the biomedical research charity, noted that the model appears to generate all the various cell types that contribute to early-stage tissue development.
However, both the researchers and scientists not involved in the study emphasize that these models should not be regarded as human embryos. The research acknowledges that the structure highly resembles, but is not identical to, the in utero situation.
Moreover, this research work has not yet been peer-reviewed.
Still, the research and other recent work shows “that models of human embryos are getting more sophisticated and closer to events that occur during normal development,” Darius Widera, an expert in stem cell biology at the UK’s University of Reading, told news agency AFP.
The work highlights “that a robust regulatory framework is more needed than ever before”, he added.
It’s important to note that the Weizmann Institute’s research does not involve implanting the models into a human or animal womb or allowing their development beyond the 14-day limit.
(With inputs from agencies)
What sets this research apart from others is its utilization of chemically modified rather than genetically modified embryonic stem cells, resulting in models that more closely resemble genuine human embryos, complete with a yolk sac and amniotic cavity.
These resemblances could make these models particularly valuable for studying conditions such as miscarriage, birth defects, and infertility, according to James Briscoe from Britain’s Francis Crick Institute. Briscoe, a principal group leader and associate research director at the biomedical research charity, noted that the model appears to generate all the various cell types that contribute to early-stage tissue development.
However, both the researchers and scientists not involved in the study emphasize that these models should not be regarded as human embryos. The research acknowledges that the structure highly resembles, but is not identical to, the in utero situation.
Moreover, this research work has not yet been peer-reviewed.
Still, the research and other recent work shows “that models of human embryos are getting more sophisticated and closer to events that occur during normal development,” Darius Widera, an expert in stem cell biology at the UK’s University of Reading, told news agency AFP.
The work highlights “that a robust regulatory framework is more needed than ever before”, he added.
It’s important to note that the Weizmann Institute’s research does not involve implanting the models into a human or animal womb or allowing their development beyond the 14-day limit.
(With inputs from agencies)